Laboratory Agar Block Decay Tests
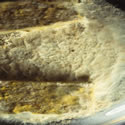
In most European based developments of wood protection agents, the agar block test is the second step in the development process. In this methodology, pure culture decay fungi are grown on agar in a sterilized environment and then the wood samples are introduced into the decay units following sterilization by some means.
The agar block decay methods are epitomized the European Standard test method EN113. This is one of the oldest test methods used in wood preservation testing. In this method, the wood samples (50x25x15mm) are exposed to a range of pure culture brown rot or white rot fungi, for 16 weeks. Scots pine is used as the wood substrate for the brown rot fungi while Beech is used in the case of white rot fungi.
Such tests are time-consuming and involve multiple steps, but can provide excellent indicative data provided the choice of test fungi and treatment levels are appropriate for the materials being tested.
It should be noted, however, that in many regions outside of Europe, the use of soil-block tests is favored over the agar-block methods.
Images
References